In the past few months, we have focused explicitly on technical analysis. We have talked about several indicators like the Relative Strength Index, momentum, and stochastic oscillator.
In this article, we will focus on an important section of fundamental analysis. We will look at what carry trade is and how traders use to make money in the financial market.
What is a carry trade strategy?
A simple definition of a carry trade is that it is a way of trading that involves borrowing a low-yielding currency and investing in high-yield currencies. So, you make money on the difference between the interest rates.
To better understand this, we need to look at how interest rates are made and how they influence the performance of currencies.
Why Interest Rates are so important
The central bank is given the mandate to set interest rates in a country. In most countries, this bank is usually independent from the elected officials to insulate it from conflicts.
In the United States, the central bank is the Federal Reserve while in Europe, the central bank is the European Central Bank.
The mandate of the central bank is to ensure stability of the financial market. They do this by regulating the financial industry and ensuring that banks have enough liquidity. They also do this by setting the ideal interest rates for the economy.
Carry trade vs arbitrage
A common question is on the difference between carry trade and arbitrage. The main difference is that carry trade is a form of arbitrage because it takes advantage of the spread between interest rates.
One of the main differences is that the carry trade strategy allows traders to make profitable trades even when the market is (relatively) stable and has low volatility.
Why? Because this strategy is not so much based on market prices, but rather on borrowing money from a country with a low interest rate currency and buying another one that provides a higher rate of return at the same time. A couple of famous examples are NZD/JPY and AUD/JPY.
There are other types of arbitrage in trading. They include risk arbitrage, statistical arbitrage, triangle arbitrage, and political arbitrage, among others. For example, risk arbitrage involves borrowing from high-risk environments and investing in low risk environments.
The Monetary Policy
A lose monetary policy is made when the economy is in trouble. For example, in the current coronavirus crisis, most central banks have brought interest rates to zero. In some countries, central banks have brought rates to negative territory.
On the other hand, these banks tighten or hike interest rates when the economy starts to improve. The goal of doing this is to prevent the economy to overheat. Also, by raising rates, the central banks give themselves firepower to use when the economy starts to deteriorate again.
Therefore, participants in the market use the carry trade strategy by borrowing a currency of a low-yielding country and buying those from higher-yielding countries.
Practical Examples
Let us first look at a basic example of a carry trade. You go to a bank and borrow $10,000 and the bank charges you a 1% interest rate per year. You then use the borrowed funds and invest in a bond that returns 5% per year. By doing this, you have just earned yourself a return of 4%.
Another example of carry trade is what happens in interest rates between the United States and Japan. Before the coronavirus crisis, the Federal Reserve had hiked interest rates to more than 2.5%. The Bank of Japan, on the other hand had left interest rates at -0.1%.
This means that there was a spread of 2.4%. Therefore, many participants were borrowing Japanese yens and investing them in US bonds. As a result, the yen weakened due to increased demand from international buyers.
» Related: How to trade Bonds
A good example of this is what happened in 2018 when the Fed hiked interest rates four times. As it did this, the USD/JPY pair rose because of the increased spread between US and Japanese interest rates. This changed in December, when the Fed suddenly turned bearish.
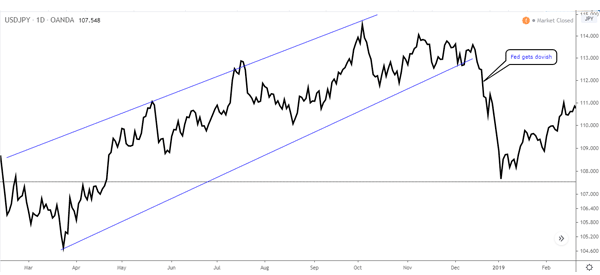
These carry trade operations are done by large hedge funds and institutional investors because they can easily borrow the currency and invest in high-yielding debts.
Still, traders can easily benefit by carefully following central banks make decisions. Other popular carry trade pairs are USD/CHF and USD/ZAR.
Carry Trade: Risks and Benefits
A carry trade strategy is a form of interest rates arbitrage because it seeks to benefit from different interest rates of countries. It is a popular trade among traders because it works most of the times.
However, its biggest risk is that central banks can change interest rates without any forward guidance.
Forward Guidance
Forward guidance refers to hints that a central bank makes about future interest rates. For example, in 2021, as the US was emerging from the pandemic, the Federal Reserve hinted that it would hike interest rates in 2023. Therefore, in all meetings it held, investors were aware about what the central bank would do.
After the 2008/9 crisis, most central banks like the European Central Bank (ECB) and Bank of England (BOE) embraced the concept of forward guidance.
However, at times, a central bank can change its policy without warning. A good example is what the Swiss National Bank (SNB) did in 2015 when it removed the peg from the euro.
Changes in economic situation
The other risk for carry trade is a sudden change in economic situation. For example, after the Covid-19 pandemic broke, many central banks like the Fed, BOJ, BOE, and SNB decided to lower interest rates. This narrowed the spread between the respective rates.
On the other hand, the main benefit of carry trade is that it has lower risks than other forms of day trading.
Risk management in carry trade strategy
Like all trading strategies, there are several risk management strategies you can use to reduce your risks. First, you should ensure that you don’t risk more than 2% of your account in a single trade. For example, if you have a $10,000 account, ensure that you are not risking more than $200 per trade.
Second, while carry trade is a relatively safe trading approach, ensure that you use minimal leverage. This is because being overleveraged can cost you a lot of money if the trades don’t perform as expected.
Third, ensure that you size your trades well. As a beginner, you should start with a small amount of lot sizes and then increase it as you gain more experience.
Summary
Carry trade is a popular trading strategy among highly sophisticated money managers. However, as shown above, it is a relatively simple strategy that any trader can use. We have looked at what it is, how to use it, and its difference with arbitrage.
External Useful Resources
- Other info about Carry Trade – Investopedia
- Carry Trade: The Multi-Trillion Dollar Hidden Market – Forbes
