Traders use several types of orders in the financial market. For starters, an order is simply a request sent to the broker asking them to initiate a trade.
For example, if you go to a grocery store, you can tell the seller to sell you an item at the current price. This is known as a market order. Alternatively, you can tell the seller to sell you the item when its price drops to a certain level. This is known as a pending order.
The main types of orders are:
- market orders
- limit orders
- stop loss
- stop limit orders
Here we go to see the fundamental differences between stop orders and stop limit orders.
What is a market order?
A market order is an order that initiates a trade at the current price. For example, if Apple shares are trading at $116, a market order will initiate the order at the current price. The main risk for a market order is known as slippage, which is a change of price between the moment of initiation and when it is executed.
This slippage tends to happen more for penny stocks and other volatile assets like cryptocurrencies. Market orders can only be placed during market hours.
Stop order
A stop order is an order to initiate a trade when the price reaches a specific level. For example, if Apple shares have been ranging at $116 and you believe that a breakout will happen at $120, you can direct the broker to initiate a trade at this point.
If you do this, the broker will open a buy trade at $120, which then becomes the market order.
Sell Stop Order
Similarly, if you believe that a new downward trend will start at $115, you can initiate a sell stop order. This simply means that if the price reaches the $115 level, a trade will be initiated.
The benefit of using a stop order is that it saves you time because you don’t need to sit in front of your computer waiting to initiate the order. Also, it is a good strategy to prevent slippage especially in high volatility markets.
Additionally, a stop order can be used in premarket trading to put positions that will be implemented when the price reaches a certain level. The chart below shows how a sell and buy stop orders works.
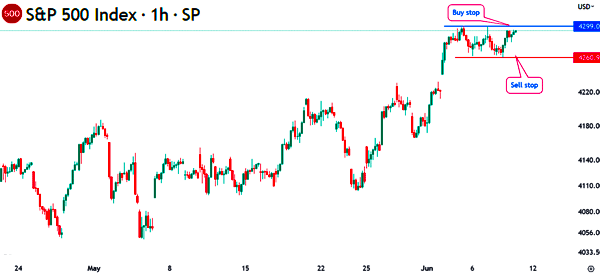


In this case, the S&P 500 index has found strong support and resistance levels at $4,260 and $4,299. Therefore, if you believe that the index will drop further below $4,260, you can place a sell stop at this level.
In this case, if the index drops to this level, the broker will need to activate a sell stop order. You will be in the money if the index continues falling.
On the other hand, you can place a buy stop trade at $4,299. If the price jumps to this level, a bullish trade will be triggered.
Limit order
A limit order is similar to a stop order but there is a limit. It simply means that you want to buy a stock but there is a limit to how much you are willing to pay for it.
For example, assume that Apple shares are trading at $116, you can place a buy limit order at $112. This means that the trade will not be executed until it moves to or below this price. This is known as a buy limit order. On the other hand, in this case, you can short the stock if its price reaches $120.
In this case, if your buy stop worked, it means that you will have bought the stock at $112. Now, if the price then rises to $120, a sell limit will be initiated. The chart below also shows how a limit order works.



In this case, you can assume that the stock will drop to the support at $4,260 and then resume the bullish trade. As such, you could place a buy limit at $4,260 and the broker will implement a bullish trade when this happens.
The other option is where you believe that the index will rise to $4,299 and then resume the bearish trend. As such, you can set a sell-limit order at this point. This trade will be profitable when the shares resume the downward trend.
What is a stop limit order?
A stop limit order combines concepts of limit orders and stop loss orders. Let us show it with an example (or take a look at what a stop limit order is). As mentioned above, a stop order and a limit order places a trade above or below the current level.
In a stop limit order, a trade is triggered when the stock rises or falls to a certain level. When this happens, the limit order is then executed at a certain pre-set level.
Assume that the stock price of a company is trading at $40 and you are unsure of the direction it will take. So, you wait for the stock to create a well-defined direction.
If it reaches $35, you believe that the stock has created a downward trend. So, you can put a stop limit order at $38. In this case, the broker will sell short the stock at a price below $38 and you can benefit when the price drops. Here is a good example of a stop limit order.
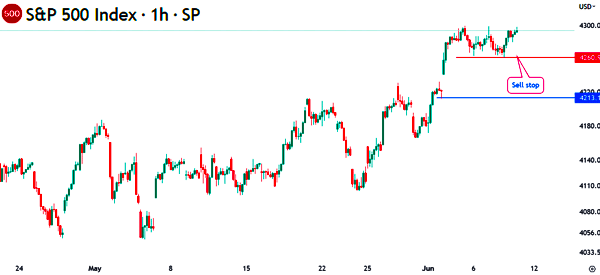

In this case, you can place a sell-stop at $4,260 and a buy limit at $4,213. The sell-stop will be triggered if the price moves to that level. Then, the buy limit will be initiated at $4,213 if you hope that the asset will resume the bullish trend when it reaches that point.
What is a trailing stop?
To understand what a trailing stop is, it is important to look at what a stop loss is. A stop loss is a tool that stops a trade automatically when it reaches a certain loss level. For example, if you place a buy trade at $10, you can place a stop-loss at $8.
A trailing stop works in the same format. The only difference is that it moves with the chart. It works well since it captures the profit so that when there is a reversal, the initial profits are captured.
Final thoughts
Stop and limit orders are excellent ways to participate in the financial market. Indeed, they are the main options used by most experienced brokers.
If you trade on a part time, you can analyze your stocks in the morning and set the stop and limit orders before you leave for work. In this case, if you also incorporate stop loss, your trades will continue to run throughout the day.
External useful Resources
How does a stop order and a stop limit order differ? – Investopedia
